Describe Methods Used to Control Vector-borne and Zoonotic Diseases
This may sound like a simple thing to do but the truth is many people do not wash their hands when they should or they do not wash for long enough. Applying modeling in prediction of pathogen replication and pathogenicity vector monitoring and control and disease transmission patterns are critical in monitoring controlling and responding to outbreaks of these diseases.
Difference Between Zoonotic Diseases And Vector Borne Diseases Difference Between
Many of vector-borne diseases are preventable through protective measures and community mobilisation.

. Prevention of Vector-borne Diseases. Control of vector-borne zoonotic diseases needs combined efforts by clinicians and public health officials to treat patients and promote behaviour likely to minimise risk of infection and by disease ecologists urban planners and medical entomologists to advise on development restoration of ecological communities and vector control to reverse the ecological drivers of. ADHS The Vector-Borne Zoonotic Diseases program is responsible for monitoring controlling and preventing diseases transmitted from animals or arthropod vectors to humans.
Wear light-coloured long-sleeved shirts and long trousers tucked into socks or boots and use insect repellent on exposed skin and clothing to protect yourself from being bitten by mosquitoes sandflies or ticks. Vectors and vector-borne diseases are found throughout the world. However no computerized translation is perfect and is not intended to replace traditional translation methods.
Vectors can transmit infectious diseases either actively or passively. A vector is a living organism that transmits an infectious agent from an infected animal to a human or another animal. The Division of Vector-Borne Diseases DVBD works to detect and prevent diseases spread by mosquitoes ticks and fleas.
Control of vector-borne zoonotic diseases needs combined efforts by clinicians and public health officials to treat patients and promote behaviour likely to minimise risk of infection and by disease ecologists urban planners and medical entomologists to advise on development restoration of ecological communities and vector control to reverse the ecological drivers of. Indoor residual spraying is the primary method of control as its effects are rapid. Vector control is the principal method available for controlling many VBDsboth historically and today.
With input from these groups we develop. Vaccines should be developed for protection against disease-causing viruses. Vector-Borne diseases can be prevented in the following ways.
Insecticidal treatment of habitat. Vector-borne and zoonotic diseases are caused by viruses bacteria or parasites that are transmitted to humans from animals or insects. The following is a list of the top ten ways you can reduce the risk of zoonotic diseases.
Globally hundreds of millions of cases and over 700000 deaths occur from vector-borne diseases annually 2 3. Moreover for some diseases such as dengue a vaccine is licensed but is not widely used due to safety concerns chikungunya Zika and West Nile disease vector control is currently the only method available to protect populations. Biological vectors such as mosquitoes and ticks may carry pathogens.
Flores and ONeill review novel approaches to control mosquito-transmitted diseases with a focus on control methods that are based. Spraying of residual insecticides typically either pyrethroids carbamates or organophosphates indoors for malaria and Aedes-borne disease control. Vectors are frequently arthropods such as mosquitoes ticks flies fleas and lice.
The most well-known diseases include dengue malaria chikungunya yellow fever and Zika from mosquitoes. Insect repellants such as DEET or Permethrin can be applied to the skin and clothes respectively. 149 Evidence-based models that include vectorhost interaction host immunity pathogen evolution and land use as well as socioeconomic drivers of transmission human behavior and adaptive capacity are.
Tick checks should be performed after exposure to dogs cats cattle and mice. Land use and increasing human populations exert selective pressure on vector-borne pathogens to be able to infect and be transmitted by people and vectors associated with human development Control of vector-borne zoonotic diseases needs. We provide public health workers with expertise support and resources for preventing and.
Working to monitor prevent and control diseases in Arizona through education immunization and research. Vectors Many of these vectors are bloodsucking insects which ingest disease-producing microorganisms during a blood meal from an infected host human or animal and later transmit it into a new host after the pathogen has replicated. ASTHO manages several environmental health groups including the State and Territorial Environmental Health Directors peer group the State Tribal Liaisons peer group the National Association of Vector-Borne Disease Control Officials the State Health in All Policies Group and the Climate Change Collaborative.
Disease Control Manual -. Climate and non-climate factors interact to determine the burden of vector-borne diseases on humans but the mechanisms of these processes are still poorly understood. Widespread use of insecticide-treated mosquito nets ITNs and long-lasting insecticidal nets LLINs are subsequently recommended.
Ensure your vaccinations are up to date for diseases prevalent in the area. Acute Communicable Disease Control 313 N. Quickly detects and monitors threats by working with health departments to monitor vector-borne diseases ArboNET a national surveillance system tracks vector-borne viruses in people animals mosquitoes and blood donors.
Climate Change Impacts on Vectors and Human Health. Vector control aims to limit the. Surveillance of VBD is key to measuring the effectiveness of interventions to control VBD.
Figueroa Street 212 Los Angeles CA 90012 Phone. If questions arise concerning the accuracy of the information please. Aircraft vehicle or hand-held space spraying for dengue epidemic and other Aedes-borne disease control.
Vector-borne Zoonotic Diseases. The Singapore model was based on a program initiated in the late 1960s and combined aggressive implementation of vector surveillance and control measures health education slum clearance improvements in water supply and storage practices to reduce vector breeding sites and legislation the 1968 Destruction of Disease Bearing Insects Act which later was replaced. Some diseases that originate in animals must be transmitted through a vector eg mosquito tick in order to infect a human.
A quick rinse under the tap is far from adequate.

Difference Between Zoonotic Diseases And Vector Borne Diseases Youtube

Schematic Representation Of The Various Health Disciplines Involved In Download Scientific Diagram
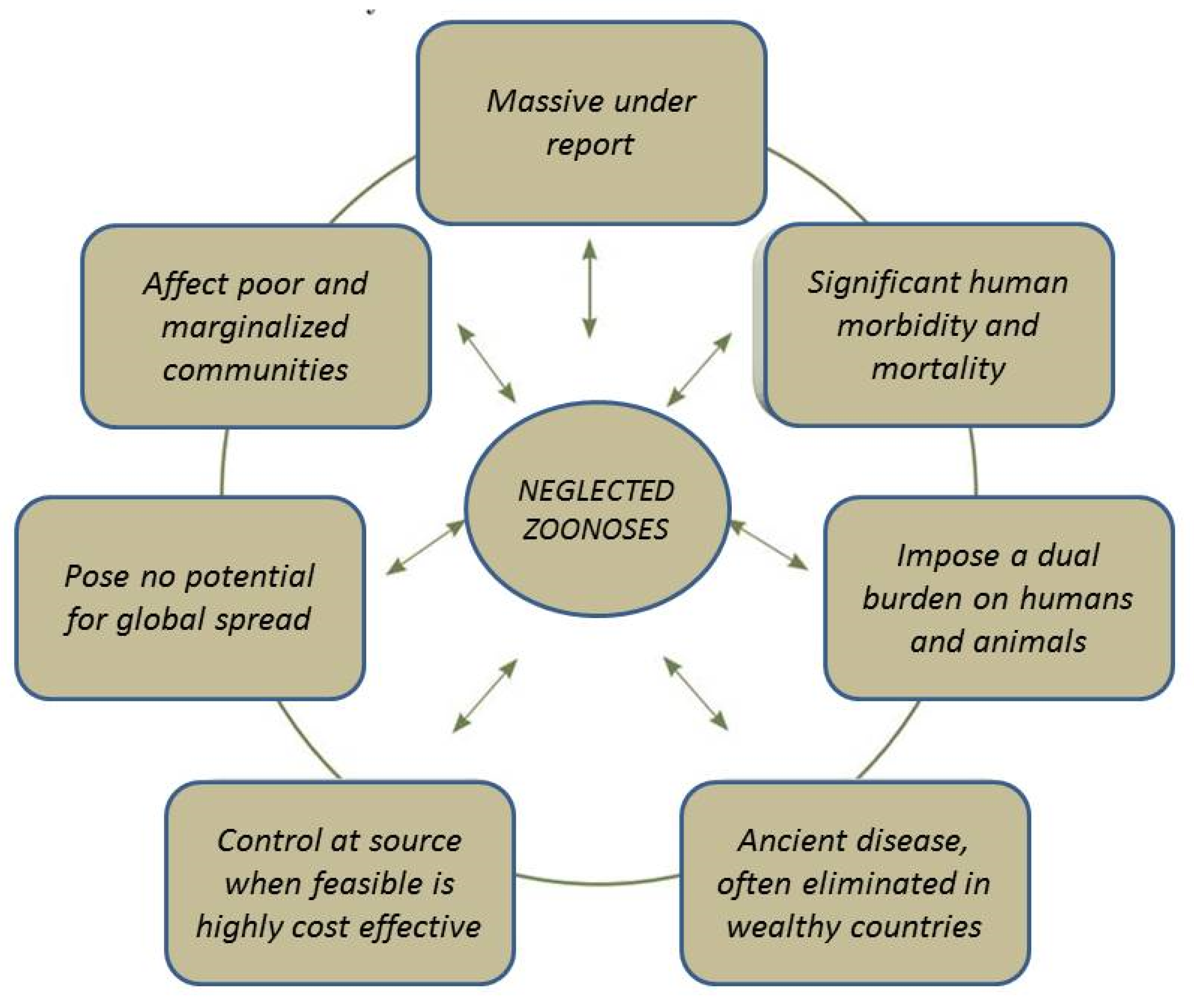
Microorganisms Free Full Text Zoonotic Diseases Etiology Impact And Control Html

Types Of Bacterial Zoonoses In Humans And Animals Representative Download Scientific Diagram
Comments
Post a Comment